 The new Euro 6 car emissions standards coming into force in September will require at least 20 sensors per auto engine, says IHS.
The new Euro 6 car emissions standards coming into force in September will require at least 20 sensors per auto engine, says IHS.
Most of the new sensors are related to exhaust aftertreatment because of new emissions laws with NOx reduction a focus alongside that of carbon dioxide.
As a pollutant, NOx has long been a stronger focus for US legislation, which also dictates that the emission parameters are measured under realistic driving cycle conditions.
But European legislators have also become tougher on this gas in recent years. IHS forecasts that the market for NOx sensors will grow at a CAGR of 9.3% during the next five years from 2014 to 2019.
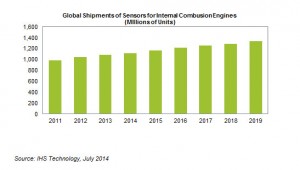
The global market for sensors used in internal combustion engines (ICE) is on the road of steady growth for the next few years, propelled by increasing utilisation in engine management and exhaust after-treatment.
Sensor shipments for engines will top 1.34 billion units in 2019, up from about 1.08 billion in 2013, as shown in the attached figure. Overall, the six-year compound annual growth rate (CAGR) from 2013 to 2019 will equate to 3.6 percent.
“Shipments of ICE sensors are growing slightly faster than car shipments,” says IHS’ Richard Dixon, “the main reason is that new concepts in emissions mitigation in the engine and in exhaust after-treatment systems require advanced sensors for their operation. Added to that, emission legislation in some major markets of the world, like China, is beginning to catch up with that of mature markets like the U.S., Europe and Japan, at least in the larger cities.”
IHS examines more than 20 sensors attached to the engine, fuel and exhaust systems of passenger vehicles. The list includes pressure sensors, devices to monitor flow and temperature, ceramic sensors for the gases nitrogen oxide (NOx) and oxygen, in addition to knock sensing, position and speed.
Among the 24 applications identified for sensors used in ICEs, several measurements have been essential to electronic fuel management systems for more than 20 years: the position of the throttle and crankshaft, the absolute air pressure of the intake manifold and the residual oxygen in the exhaust. And multiple sensor insertions are possible—depending on the pipe configuration, a gasoline engine can feature four oxygen sensors, two of which serve an on-board diagnostics function to check for correct operation, although a diesel engine still has only one oxygen sensor, located before the diesel oxygen catalyst.
The biggest category for sensing is temperature measurement, with multiple sensors to be found on exhaust systems. The technology used is typically platinum-based resistance temperature detector (RTD) sensors to withstand temperatures of up to 1,000 C (1,832 F). On average, approximately two temperature sensors are used per vehicle. At lower temperatures, negative-resistance sensors (NTC) or semiconductor integrated circuits are also deployed. Examples include engine-coolant monitoring to protect against overheating, intake air measurement or in exhaust-gas recirculation systems used to lower NOx output from the engine.
At other points in the powertrain, the fuel injection system and cylinder pressure are proving to be interesting new opportunities for pressure sensor suppliers. Although cylinder-pressure sensing has been largely too expensive for car manufacturers to adopt, IHS expects significant growth in this area in coming years, led by Volkswagen and Daimler in diesel engines. Owing to the low penetration today, growth rates in the coming five years to 2019 are high at more than a 40 percent CAGR.
The type of engine has an impact on exhaust systems. Lean-burn engines require more sensors than standard, stoichiometric engines because the exhaust aftertreatment is more complex. The high residual oxygen content in the exhaust of these engines makes it impossible for conventional three-way catalysts to reduce NOx pollutants.
Diesel and some direct injection gasoline engines fall into this category. These engines require feedback on NOx concentration in the exhaust stream as part of the emission control system. Stoichiometric engines—some direct injected engines and all modern port injected engines—do not need a NOx sensor.
In addition, many vehicles today feature some kind of forced induction—turbo- or supercharging—of the fuel/air mix. The increased use of turbochargers is the main factor enabling engines to be made smaller and less polluting.
As these boosters become more sophisticated, such as having a variable geometry, position sensing becomes important. So far, though, turbocharger speed sensing is mostly confined to the large commercial vehicle segment and is not yet widely found in cars.
For the first time, European Euro 6 legislation specifies a particle number per kilometer as a key measure, with phased-in adoption. Direct injection gasoline engines produce more hazardous particles than standard gasoline multi-port injection engines. This means that gasoline particle filters on the exhaust will be adopted in the former, along with the means for self-monitoring, which will drive the use of particle mass and possibly pressure sensors.
Particle filters have been used on diesel engines to reduce NOx since legislation in Euro 4. In particular, diesel particle filters have pressure sensors to monitor the filter when it is clogged, indicating to the engine ECU when to regenerate the filter—a process that also requires temperature sensing.
Sensor adoption also has a strong regional emphasis. As emissions standards are not yet harmonized worldwide, less stringent emission standards than those affecting U.S., Japanese or EU standards are in play, which leads to lower sensor content in emerging markets. A gasoline-engine vehicle in Iran or Malaysia, for instance, will have a much lower sensor requirement than an engine in Japan. The difference can be as many as 10 sensors.
 Anritsu’s latest optical communications network tester is a multiple protocol instrument which supports Ethernet, Fibre Channel and SDH/SONET at rates up to 10Gbit/s, as well as optical transport network (OTN) testing.
Anritsu’s latest optical communications network tester is a multiple protocol instrument which supports Ethernet, Fibre Channel and SDH/SONET at rates up to 10Gbit/s, as well as optical transport network (OTN) testing.