Knowles and Infineon dominate the market for microelectromechanical system (MEMS) microphone chips.
Knowles of the U.S. in 2013 was the biggest supplier of packaged MEMS microphones ready for assembly on printed circuit boards, according to IHS Technology.
 Germany’s Infineon, meanwhile, was the leader one layer below, supplying bare MEMS dies to MEMS microphone makers. Knowles accounted for 59 percent of the market’s total revenue among packaged MEMS microphone suppliers, while Infineon owned 78 percent of the MEMS die trade in terms of unit shipments.
Germany’s Infineon, meanwhile, was the leader one layer below, supplying bare MEMS dies to MEMS microphone makers. Knowles accounted for 59 percent of the market’s total revenue among packaged MEMS microphone suppliers, while Infineon owned 78 percent of the MEMS die trade in terms of unit shipments.
Among microphone suppliers, Illinois- based Knowles remained far and away the leader, even managing to increase its revenue share last year to 59 percent, up from 55 percent in 2012. Knowles has been particularly successful in growing its business, via high-performance microphones priced at a premium, for Samsung and particularly for Apple, which is the leading buyer of MEMS microphones and dictates supply chain dynamics in the area. Knowles supplies, for instance, two of the three high-performance MEMS microphones in Apple’s iPhone 5s, as well as one of three in the iPhone 5.
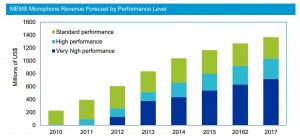
MEMS microphones are increasingly important differentiators in smartphones, with the highest-quality devices proving helpful in ambient-noise cancellation and also in delivering crystal-clear audio in high-definition video. Apple was the first to use high-performance MEMS microphones, initially seen in 2012 with the iPhone 5, with Samsung then following suit shortly afterward via its Galaxy S4 and Note 3 smartphones. MEMS microphones are now also found in tablets like the Apple iPad, as well as in Apple headsets.
At a distant second after Knowles was AAC with 13 percent revenue share, followed by No. 3 Goertek with 7 percent share; both suppliers are from China whose business also heavily depends on Apple. AAC supplies one of the three high-performance microphones in the iPhone 5 and is now in the 5s, while Goertek is the main supplier for the MEMS microphone in the headset that sells along with the iPhone. AAC grew 8 percent, and Goertek had even greater growth at 35 percent as it started delving into high-performance microphones for mobile handsets.
Meanwhile, fourth-ranked BSE of South Korea reaped the benefits of supplying to Apple rival Samsung, pushing up the microphone maker’s revenue by more than 250 percent from 2012 to 2013.
Rounding out the top five and tied in fourth place with BSE was French-Italian maker STMicroelectronics, which continued to see its MEMS microphone business expand after gaining impressive design wins in the iPad.
While Knowles, the pioneer and market leader, designs its own MEMS, an increasing number of MEMS microphone suppliers focus on packaging.
Including makers such as AAC, Goertek, BSE and Japan’s Hosiden, these companies buy a standard MEMS die and an application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC), and then package them for selling under their own brand. All four companies are manufacturers, historically, of conventional electret condenser microphones—an older technology that cannot match MEMS in performance and miniaturization important for mobile devices. The four makers have no traditional MEMS or semiconductor background, and their expertise lies in acoustics as well as assembly and packaging.
In the MEMS bare die business where Infineon rules, the German maker owns nearly three-quarters of total shipments, supplying to major customers like AAC, Goertek, BSE, Hosiden and another Chinese buyer, Gettop. Infineon’s growth is remarkable: up 204 percent in 2011; and up another 50 percent from 2012 to 2013.
Two suppliers, however, are angling for a bigger slice of the business: Omron Corp. and New Japan Radio, both Japanese-based. Omron is expanding to customers in China and Taiwan besides serving main customer STMicroelectronics, which potentially could be developing its own microphone die. For its part, New Japan Radio is gaining headway thanks to headset sales to a Korean module maker.
The bare die business, in particular, is plagued by inflated inventory building in order to compensate for yield losses at various steps of the supply chain—from the wafer dicing stage to the packaging phase, and onward to assembly on the printed circuit board.
Inventory building is especially high in the supply chain serving Apple.
“Because Apple releases a huge-selling handset every year, and given the severe penalties imposed by Apple for delays, the MEMS microphone supply chain must overestimate component supplies in order to ensure it can meet Apple’s demand,” said Marwan Boustany, senior analyst for MEMS and sensors at IHS. “This, in turn, leads to microphone inventory being accumulated at every point in the supply chain.